分层领域模型
在《Java开发手册》中,阿里巴巴对各个领域的模型都做了很详细的划分,如下:
- DO(Data Object):与数据库表结构一一对应
- DTO(Data Transfer Object):数据传输对象,Service或Manager向外传输的对象
- BO(Business Object):业务对象,由Service层输出的对象
- Query:数据查询对象
- VO(View Object):显示层对象
了解了上面几种类型的划分,在工作中使用的话,避不可免的就会出现对象之间的转换。市面上有几种常见的对象转换工具库类:
- Apache BeanUtils
- Spring BeanUtils
- Cglib BeanCopier
- Dozer
- orika
- MapStruct
这些转换工具各有优劣,一般情况下,如果不追求性能,而且是较少使用的话,我们直接使用Spring提供的工具就可以了。如果大批量的出现复杂对象复制,可以使用Dozer,orika这种重量级的工具。 MapStruct就是属于性能好,而且用起来也不算特别麻烦的那种,相较于重量级的来说。
MapStruct
摘自官网:
MapStruct是一种代码生成器,它基于约定优于配置的方法,极大地简化了Java bean类型之间映射的实现。
生成的映射代码使用普通的方法调用,因此快速、类型安全且易于理解。
从介绍来看,它是通过额外自动生成的代码,来完成对象的复制的。
原理
MapStruct属于在编译期,生成调用get/set方法进行赋值的代码,生成对应的java文件。在编译期间消耗少许的时间,换取运行时的高性能
使用
配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| <properties>
<mapstruct.version>1.4.2.Final</mapstruct.version>
<lombok.version>1.18.12</lombok.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct</artifactId>
<version>${mapstruct.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<configuration>
<annotationProcessorPaths>
<path>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-processor</artifactId>
<version>${mapstruct.version}</version>
</path>
<path>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>${lombok.version}</version>
</path>
</annotationProcessorPaths>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
|
定义两个实体类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Education education;
private Integer age;
}
public class UserVo {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String education;
private int age;
}
|
定义转化接口类Mapper文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
import org.mapstruct.Mapper;
import org.mapstruct.factory.Mappers;
@Mapper
public interface UserConvert {
UserConvert INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(UserConvert.class);
@Mapping(source = "name", target = "username")
UserVo convert(User user);
}
|
具体使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setEducation(Education.A);
user.setName("xin");
user.setAge(10);
UserVo convert = UserConvert.INSTANCE.convert(user);
System.out.println(convert);
|
编译生成的源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
public class UserConvertImpl implements UserConvert {
@Override
public UserVo convert(User user) {
if ( user == null ) {
return null;
}
UserVo userVo = new UserVo();
userVo.setUsername( user.getName() );
if ( user.getId() != null ) {
userVo.setId( String.valueOf( user.getId() ) );
}
if ( user.getEducation() != null ) {
userVo.setEducation( user.getEducation().name() );
}
return userVo;
}
}
|
通过观察自动生成的代码,它也就是实现了我们之前声明的接口,然后通过getter和setter对属性进行一一赋值。
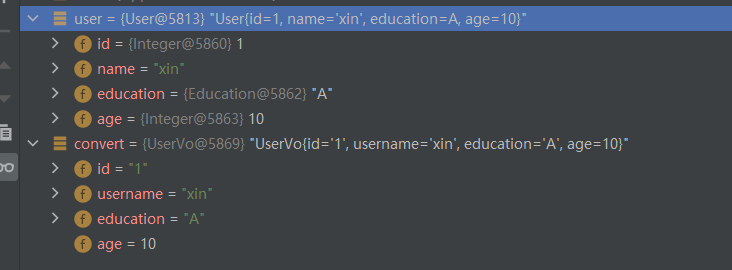
打印输出的对象和源对象,可以看到,这是生成了一个新的对象,也就是深度拷贝,基本类型与包装类型的属性也可以进行自动转换,包装类型与String也可以转换,枚举类型只是获取了枚举类的name进行了赋值
性能比较
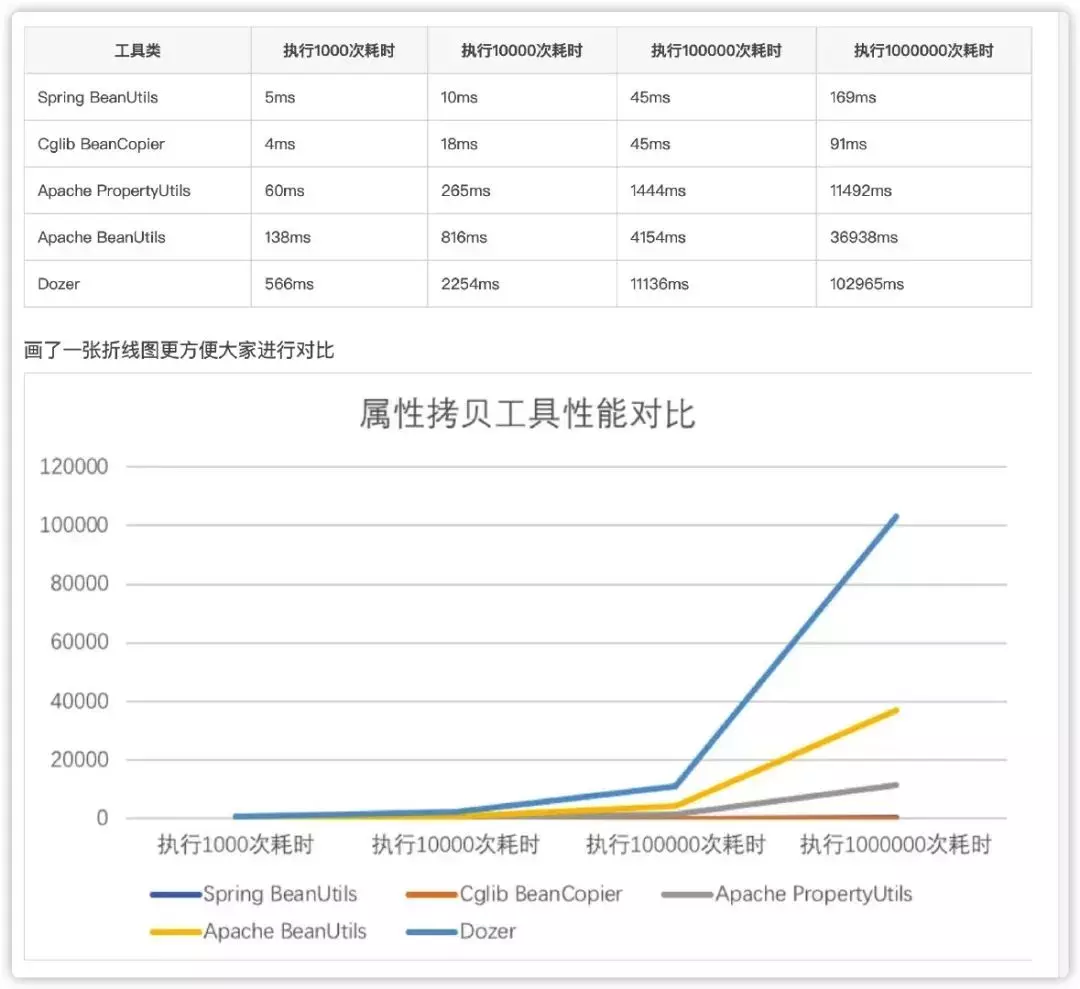
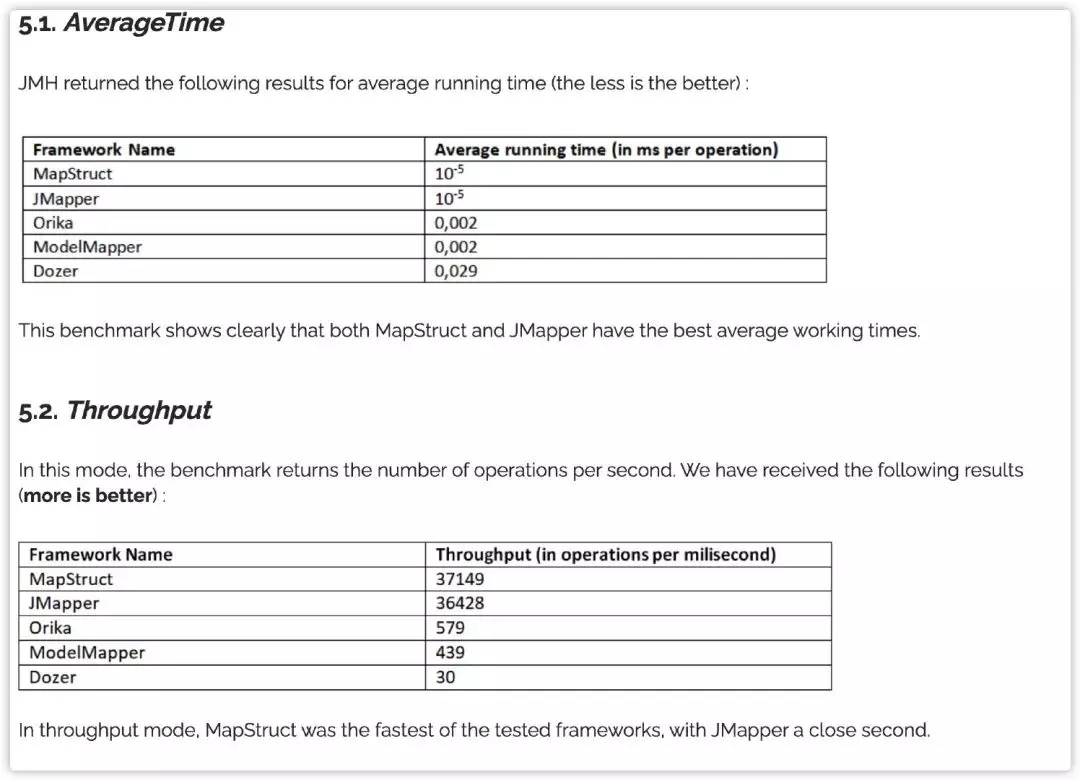
可以看出,MapStruct的性能是相当优秀的
后续会继续更新。。。
参考
https://my.oschina.net/u/4047016/blog/4528088
https://github.com/mapstruct/mapstruct-examples (MapStruct的例子)
https://mapstruct.org/ (MapStruct官网)




